It’s time to do your Math homework. You look down at your page. The question tells you: “Find the perimeter of this right triangle."
You think to yourself:
What's the perimeter again?
How do I find it?
And why aren’t all the sides labelled?
 Math can be very stressful for many people. Knowing the proper methods will help you get it right — just like the triangles you’re working with!
Math can be very stressful for many people. Knowing the proper methods will help you get it right — just like the triangles you’re working with!
Reviewing Key Terms
Before we can learn how to find the perimeter of right triangles, we need to know what “perimeter” and “right triangle” even means.
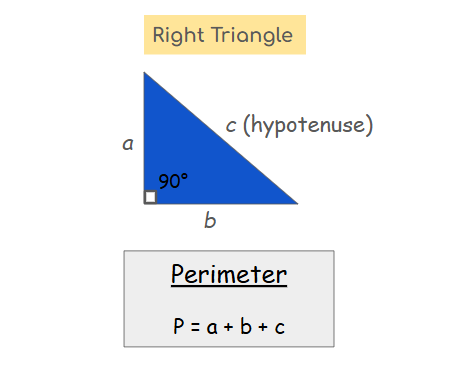
Here’s a few reminders of some helpful math vocabulary when calculating the perimeter of right triangles:
Perimeter: the total distance around the outside of the triangle (or any other 2-D shape). Some common units for perimeter (depending on the measurements for the sides) are:
meters (m), centimeters (cm), kilometers (km)
inches (in), feet (ft), yards (yd), miles (mi)
Right angle: an angle that measures 90 degrees
Right triangle: a triangle that has a 90° angle
Hypotenuse: the longest side in a right triangle (hint: it’s across from the right angle)
Pythagorean theorem: a formula for solving right triangles
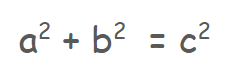 Remember that a, b, and c are variables — these letters hold the place for whatever numbers or values that need to be plugged into this formula. In the Pythagorean theorem:
Remember that a, b, and c are variables — these letters hold the place for whatever numbers or values that need to be plugged into this formula. In the Pythagorean theorem:
c = the hypotenuse or longest side of the right triangle
a & b = the other 2 shorter sides or legs of the triangle
Knowing these key terms and concepts will make finding the perimeter of right triangles much easier.
Case 1: All The Sides Are Given (Same Units)
Now that we reviewed some of our math words, it’s time to start learning how to solve some Math problems.

Sometimes your teacher will ask you to find the perimeter of a right triangle and label all the side lengths, like the one in the example below:
To solve this type of problem, all you need to do is add up all 3 side lengths:
4.5 m + 6 m + 7.5 m = 18 m
The perimeter of this triangle is 18 m
Check out this video if you need a review on how to add decimals!

In general, you can use this formula to find the perimeter of any triangle — not just a right triangle:
Perimeter of a triangle = side A + side B + side C
Case 2: All The Sides Are Given (Different Units)
 Other times, your teacher might ask you to find the perimeter of a right triangle and give you all the side lengths, but some have different units.
Other times, your teacher might ask you to find the perimeter of a right triangle and give you all the side lengths, but some have different units.
Don't panic! We'll walk through an example together...
Step 1
Check to see if all units are the same.
In this example:
2 of the sides are in m
1 side is in cm
Step 2
Convert or change the side lengths with different units so that ALL sides are the SAME units.
In this example, I need to change or convert 300 cm to m. Since there are 100 cm in 1 m, I know that 300 cm = 3 m.
Check out this Math Reference Sheet for some common conversions (metric and US units)
Step 3
Add up all the side lengths (same units) to calculate the perimeter.
After converting, the side lengths to use are: 3 m, 4 m and 5m. So:
Perimeter = 3 m + 4 m + 5 m = 12 m
Quiz
Maya uses her ruler to measure the sides of a right triangle. They're 50 mm, 4 cm, and 3 cm. She wants to find the perimeter of this right triangle. What should Maya's first step be?
Case 3: 2 of 3 Sides Are Given (Same Units, Missing Hypotenuse)
Sometimes your teacher will ask you to find the perimeter of a right triangle, but only give you measurements for 2 of the 3 sides.
 Don’t worry, they’re not asking you to do the impossible! There’s just one more step you need to do before calculating the perimeter. It involves our handy dandy Pythagorean theorem!
Don’t worry, they’re not asking you to do the impossible! There’s just one more step you need to do before calculating the perimeter. It involves our handy dandy Pythagorean theorem!
Let's look at an example:
Step 1
Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the third side.
In this example, we need to find the hypotenuse (Side c) of the right triangle.
a = 6 m, b = 8 m, c = ?
When you plug in your numbers, you should get 6² + 8² = c²
Time to calculate for c!
First calculate the left squared numbers: 6² = 36 and 8² =64:
So, 6² + 8² = 36 + 64 = 100
Since 6² + 8² = c², this means 100 = c²
Careful here! You're not quite done. Since we want to find c (not c²), we need to find the square root of this number: c = √100 = 10.
So, c= 10 cm
Watch the video below to see these steps for finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle using Pythagorean theorem.
Step 2:
Add up your side lengths to calculate the perimeter of the right triangle:
6 m + 8 m + 10 m = 24 m
So, the perimeter of this right triangle is 24 m
Case 4: 2 of 3 Sides Are Given (Same Units, Missing Side but Hypotenuse Given)
 What should you do if you know the hypotenuse but not one of the shorter sides of the right triangle? Take a look at the example below:
What should you do if you know the hypotenuse but not one of the shorter sides of the right triangle? Take a look at the example below:
Step 1
Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the third side.
In this example, we need to find one of the legs or shorter sides of the right triangle:
a= ?, b= 5 yards, c= 13 yards
When you plug in your numbers, you should get a² + 5² = 13²
Time to calculate for a!
Note: This is slightly different from finding the hypotenuse or c.
First, calculate the squared numbers: 5²=25 and 13²=169:
So, a² + 25 = 169
To find a², we need to move 25 (or b²) to the other side of the equation. We can do this by subtracting it from both sides:
a² + 25 - 25 = 169 - 25
This becomes a² = 169 - 25 since +25 and -25 cancel out to give 0
Now, we have a² = 169 - 25 = 144
So, a² = 144
Just like in Case 3, we're not done quite yet! We need to find a (not a²), so we need to find the square root of this number:
a = √144 = 12.
So, a= 12 cm
Watch the video below to see these steps for finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem:
Step 2
Add up your side lengths to calculate the perimeter of the right triangle.
12 yds + 5 yds + 13 yds = 30 yds
So, the perimeter of this right triangle is 30 yds
Quiz
Ms. Newton draws a right angle on the board. She labels the legs of the right triangle 9 in. and 12 in. What is the perimeter of this right angle triangle?
Take Action
Practice makes perfect! Doing more questions will help you build confidence and get extra practice. Try a mix of questions from each of the different cases we explored this Byte!
Pro tip: Make sure you know where to find the squared (²) and square root (√) buttons on your calculator to make calculations quicker and easier for you.

It’s time to ace your next math test!
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
